Vehicles That Weigh Around 6000 lbs: Tax Benefits and Options
When you’re in the market for a vehicle that balances power and efficiency, those weighing around 6000 lbs often stand out. These vehicles offer a unique blend of robustness and versatility, making them ideal for various needs, from family road trips to heavy-duty tasks. Whether you’re eyeing a sleek SUV or a rugged truck, understanding the weight class can help you make informed decisions.
The 6000 lbs range often includes both light and heavy-duty vehicles, providing options for different lifestyles and requirements. This weight class can influence factors like fuel efficiency, towing capacity, and overall performance. It’s crucial to consider these aspects when choosing a vehicle that fits your needs while offering the reliability and strength you seek.
Exploring vehicles in this weight range opens up a world of possibilities, offering a balance between durability and practicality. Dive into the details to discover which models best align with your driving demands and preferences.
Key Takeaways
- Vehicles around 6000 lbs offer a balance of power, efficiency, and versatility, making them ideal for both personal and business use.
- Understanding the weight class helps assess vehicles’ performance, fuel efficiency, and towing capability, which are key for effective decision-making.
- Vehicles exceeding 6000 lbs GVWR may qualify for significant tax benefits under IRS Section 179, which can provide substantial financial savings.
- Popular models like the Audi Q7, Ford Explorer, and Jeep Wrangler offer benefits like enhanced towing capacity and stability due to their weight.
- Tax deductions necessitate compliance with business use criteria and proper documentation, making it essential to consult tax professionals for efficient claims.
Understanding the Importance of Vehicle Weight
Vehicle weight significantly impacts performance, efficiency, and eligibility for benefits like tax deductions. For vehicles around 6,000 lbs, this weight determines their classification and application.
Performance and Efficiency
Weight affects how vehicles handle, accelerate, and consume fuel. Heavier vehicles like the Audi Q7 and Bentley Bentayga have enhanced stability and towing capacity but might have lower fuel efficiency compared to lighter counterparts. Consider this balance when evaluating vehicle needs.
Tax Benefits and Eligibility
Vehicles weighing between 6,001 and 14,000 lbs qualify for substantial tax deductions if used for business. Under IRS Section 179, the deduction can reach up to $30,500, depending on compliance with business use requirements. Ensure the vehicle is used primarily for business and placed into service within the same tax year claimed.
Compliance and Verification
Confirm the Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) by checking the driver’s door, as stated by manufacturers. This information ensures compliance with legal classifications for regulatory purposes.
Industry Classifications
Understanding weight classifications helps in determining vehicle types—Light Duty (GVWR ≤ 10,000 lbs) to Medium Duty (10,001–14,000 lbs)—and their implications on emissions standards.
Explore various models in this weight range to meet your specific driving requirements, balancing performance and legal advantages.
Tax Incentives for Vehicles Over 6000 lbs
Discover the valuable tax benefits available for vehicles over 6,000 lbs GVWR. These tax incentives, particularly under Section 179, can significantly reduce your taxable income when you own a qualifying vehicle for business use.
Overview of Section 179 Deduction
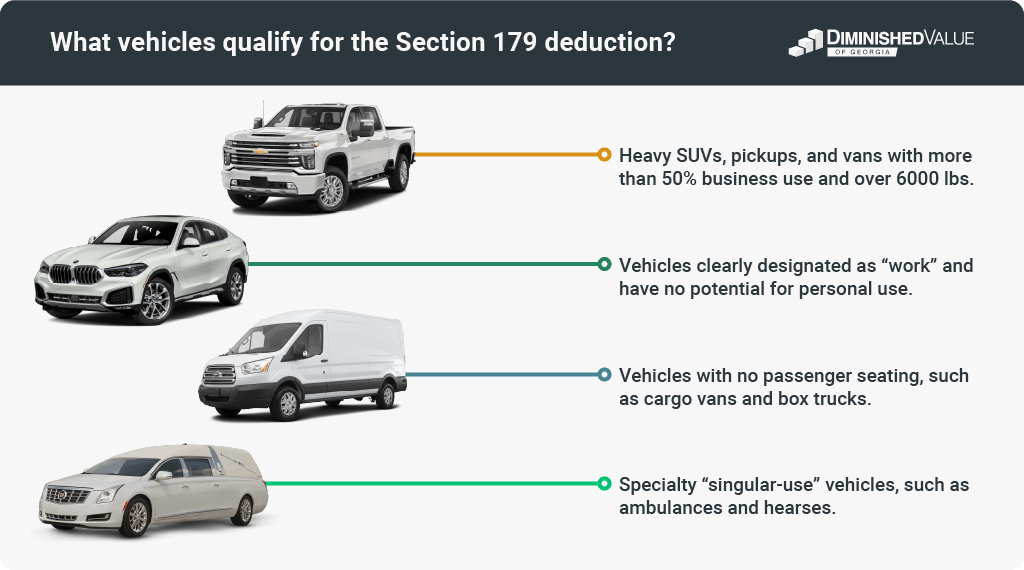
The Section 179 deduction allows you to write off the entire cost of eligible vehicles in the purchase year. Heavy vehicles like SUVs, pickups, and vans with a GVWR of 6,000 lbs or more qualify, offering businesses immediate financial relief. Instead of spreading the deduction over several years, you can deduct up to $27,000 for the 2022 tax year and $28,900 for the 2023 tax year.
Criteria for Qualifying Vehicles
To qualify for these tax incentives, ensure your vehicle meets specific criteria:
- Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR): The vehicle must have a GVWR of 6,000 lbs or more.
- Business Use: Use the vehicle primarily for business, at least 50% of its operation should be business-related.
- Purchase and Service Date: The vehicle must be purchased and placed in service within the tax year for which you seek the deduction.
Eligible vehicles include various models such as the Audi Q7, Bentley Bentayga, and Cadillac Escalade, known for their robustness and space. For detailed confirmation of a vehicle’s eligibility, consult with a tax advisor. This ensures all temporal and usage requirements are met effectively for your business’s benefit.
Popular Vehicles Weighing Around 6000 lbs
When browsing vehicles, those tipping the scales around 6,000 lbs stand out for their versatility and performance. These vehicles often qualify for tax deductions while delivering robust power and functionality.
SUVs and Trucks
Several SUVs and trucks surpass the 6,000-lb mark, making them prime candidates for Section 179 tax benefits. Here’s a glimpse of some popular models:
- Ford Explorer: Depending on the engine, the GVWR varies from 6,060 to 6,150 lbs.
- Jeep Wrangler: Features a 6.4-liter V8 engine with a GVWR of around 6,400 lbs.
- Toyota 4Runner: GVWR between 6,100 and 6,300 lbs makes it a strong contender.
- Chevrolet Tahoe: Exceeds the 6,000-lb threshold, with a GVWR of 7,400 to 7,500 lbs.
SUVs and trucks in this weight range offer enhanced stability, crucial for towing and off-road adventures, contrary to lighter vehicles.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Considering a vehicle’s weight is crucial for selecting one that meets your needs. Vehicles around 6,000 lbs usually balance power and efficiency:
- Performance: Heavier vehicles like the Dodge Durango (6,500-7,100 lbs GVWR) often boast superior towing capacity, appealing for those who need to haul trailers or boats.
- Stability: Larger SUVs provide a grounded feel, important for highway driving and rough terrain.
- Fuel Efficiency: Though heavier, models like the BMW X5 (6,173-7,055 lbs GVWR) maintain competitive fuel efficiency, offering a mix of power and economy.
Understanding these factors helps you make informed decisions and match vehicle capabilities to your driving and business needs.
Claiming Tax Deductions Successfully
To leverage tax deductions for vehicles weighing around 6,000 lbs, understanding Section 179 and bonus depreciation processes is crucial. Proper filing and record-keeping ensure successful claims.
Steps to File for Section 179
- Purchase and Place in Service: Acquire and put the vehicle into business use within the tax year in question.
- Verify Business Use: Confirm that the vehicle is used over 50% for business purposes. Otherwise, it won’t qualify for Section 179.
- Complete Form 4562: Fill out IRS Form 4562 accurately. Include details like vehicle cost and depreciation on this form.
- Attach Form to Tax Return: Submit the Form 4562 with your tax return. Adhere to IRS instructions for claiming the deduction.
- Review for Accuracy: Double-check all entries and calculations. Errors might delay processing or affect your deduction.
- Bonus Depreciation: Section 179 may be supplemented by bonus depreciation. This element allows additional write-offs on qualified property within the same tax year. Ensure compliance with specific eligibility.
- Maintain Thorough Records: Secure detailed records of the vehicle’s business use, purchase receipts, GVWR documentation, and filed forms. These documents may be necessary for future audits or related tax preparation.
- Consult Professionals: Engage an accountant or tax advisor. They can provide insights on depreciable values, prepare accurate documentation, and confirm IRS guidelines are met. This practice maximizes your deductions while minimizing liabilities.
Business Use and Eligibility
Vehicles weighing over 6,000 lbs may qualify for tax benefits under IRS Section 179 if they meet specific criteria related to business use and weight. This section explores how to determine business use and understand the limitations on deductions.
Calculating Business-Use Percentage
To determine the deductible amount for Section 179, calculate your vehicle’s business-use percentage. Divide the total miles driven for business purposes by the total miles driven (including personal use) during the year. You then apply this percentage to the vehicle’s purchase price. For instance, if your vehicle’s purchase price is $50,000 and your business-use percentage is 60%, your deductible amount is $30,000. Note that business use must be at least 50% to qualify for these deductions.
Limitations and Caps on Deductions
Understanding the limitations and caps on deductions is essential for maximizing your tax benefits. For 2024, the maximum Section 179 deduction is $1,220,000, with a spending cap of $3,050,000 on total equipment purchases. Deductions begin to phase out once purchases exceed the spending cap. Additionally, bonus depreciation, offering a 60% first-year deduction, may apply to some vehicles, though it’s limited for heavy SUVs and vehicles under the 6,000 lbs GVWR threshold. Always consult with a tax professional to navigate these constraints effectively.
Conclusion
Exploring vehicles around the 6,000 lbs mark presents a unique opportunity to balance power, efficiency, and financial benefits. Whether you’re drawn to the stability and towing capacity of heavier models or the efficiency of lighter options, there’s a vehicle to meet your needs. Keep in mind the potential tax advantages under Section 179, which can significantly impact your business finances. As you weigh your options, consider consulting with a tax advisor to fully leverage these benefits. By carefully selecting a vehicle that aligns with your driving demands and business requirements, you can enjoy both enhanced performance and substantial savings.